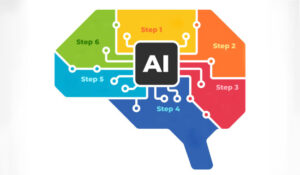
Gennadiy Bezko at MiaRec explains the contact centre AI maturity model.
In 2023, contact centre leaders caught the Artificial Intelligence (AI) bug, realizing the many benefits that Conversational and Generative AI can bring.
According to Gartner, the “global conversational AI and virtual assistant market represents the fastest-growing segment in the contact centre forecast, helping to spur 24% growth in 2024.”
Furthermore, the report explains that contact centre decision makers are planning to invest heavily in conversational AI as they are trying to reduce the reliance on live agents.
However, we are still far away from a future of fully AI-run contact centres. “Overall, Gartner estimates around 3% of interactions will be handled via CC [Contact Center] AI in 2023, growing to 14% of interactions in 2027.”
Although contact centre decision makers know they want to invest in Conversational AI, they are struggling to know what the adoption journey will look like and how to phase investment decisions.
Here at MiaRec, we talk to dozens of large companies, financial institutions, and government agencies every week who are asking us all the same question: “How do we start?”
Over the past few weeks, my team and I sat down and developed the Contact Center AI Maturity Model that you see below as a guiding light or North Star to guide you through that maturity journey step by step.
It is our opinion on how organizations will adopt AI in a phased approach starting at simply supporting their manual QA processes, and moving on to automating and then augmenting contact centre processes, empowering their agents through knowledge, and finally shedding the mantle of being a cost centre and driving revenue themselves.
You can download the maturity model as a mini 6-slide presentation here.
So, let’s walk through each of the phases in detail.
Level 1: Supporting Manual QA Processes
Who Benefits:
Primarily supervisors (agents only indirectly)
Goal:
In this first level, contact centre operations focus entirely on enabling the single agent. The primary goal here is to increase contact centre efficiency and improve customer experiences by helping supervisors to be more efficient as they manually evaluate only 2-5% of the calls for agent performance.
In this level, Machine Learning and Large Language Models (LLMs) are used in a rudimentary way to transcribe call recordings.
Transcripts make the call recording not only searchable but supervisors and agents alike can quickly scan the transcript to get up to speed.
In addition expression syntax-based keyword spotting (e.g., competitor or product names mentioned) and topic analysis (e.g., identify all calls related to shipping problems or returns).
While AI offers limited functionality, is somewhat tedious to set up, and transcriptions were expensive until recently, it provides insights that can help with quality management.
It is important to note that no Conversational or Generative AI is used to augment customer support or contact centre operations.
Critical KPIs:
- Average Handle Time (AHT): Average duration of customer interactions, including talk time and after-call work.
- Call Abandonment Rate (AR): The percentage of calls that are disconnected by the customer before reaching an agent.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR): The percentage of customer issues resolved on the first contact, without the need for follow-up.
- Service Level/Response Time: The percentage of calls answered within a predetermined threshold (e.g., 20 seconds).
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score: A measure of how satisfied customers are with the service they received.
- Agent Turnover Rate: The rate at which agents leave the contact centre, which can indicate the overall work environment and satisfaction.
- Quality Scores: Based on call monitoring and evaluation, measuring adherence to procedures, communication skills, and problem-solving effectiveness.
Ethical Considerations & Compliance Awareness
Even at this initial level, where AI is not actively used by the contact centre staff, it’s important to think ahead and establish a foundation of AI ethics and compliance for your organization.
This will allow you to create vendor selection and evaluation criteria, but it can also involve programs to raise internal awareness and increase education for agents and supervisors about the potential future use of AI and its ethical implications.
Level 2: Simple Automation of CC Processes
Who Benefits:
Primarily supervisors; secondarily agents
Goal:
Automate the contact centre and quality assurance processes using Conversational and Generative AI to maximize efficiency without altering any existing processes.
For example, supervisors can streamline the manual QA process by utilizing AI to automatically score 100% of their customer interactions, providing support and improving overall productivity or intelligently route calls to available agents (IVR).
Critical KPIs:
- Agent Performance Improvement Over Time: Monitors the development of individual agents based on AI-derived insights and training.
- Supervisor Intervention Rate: The frequency with which supervisors need to intervene in calls: (Number of Times Supervisors Intervene / Total # of Calls) x 100.
- Quality Score Trends: Evaluates the impact of AI on the overall quality of interactions over time, based on standardized criteria.
- Training Effectiveness Score: Assesses the impact of AI-driven training programs on agent performance and skill development.
- Sentiment Analysis Accuracy: Gauges the effectiveness of AI in accurately capturing customer sentiment, which is crucial for understanding customer satisfaction.
- Call Review Efficiency: Measures the time savings and efficiency gained in the QA process due to AI-assisted call summaries and analysis.
AI Transparency and Accountability
Introduce measures to ensure that any AI tools used for transcription and call analysis are transparent in their functioning and accountable in their outputs. This is crucial for maintaining trust and adherence to regulatory standards.
Level 3: Augmenting Contact Centre Processes With AI to Maximize Productivity
Who Benefits:
Both supervisors and agents
Goal:
Maximize the contact centre’s agent and supervisor efficiency and productivity by augmenting and improving current contact centre processes with Generative and Conversational AI.
AI-powered tools, like automatic call summaries and note taking, help to streamline post-call work and auto-completing answers and auto-generated customer replies make contact centre agents much more efficient and productive during calls.
In addition, supervisors can use AI-driven sentiment analysis and trend analysis to identify calls for follow-up identify those calls that require human review or follow-up.
This allows managers to focus on high stake calls. They also benefit from better insights into VOC with call type categorization and AI topic analysis.
Critical KPIs:
- Number of Calls Evaluated (Auto Scored vs. Manual): The goal is to use Auto QA for 100% call scoring to monitor and improve agent performance.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR): Measures the effectiveness of AI-assisted agents in resolving customer issues during the first interaction, indicating improved efficiency in handling calls.
- Average Handle Time (AHT): Tracks the average duration of customer interactions, including talk time and after-call work, which is expected to reduce due to AI-powered call summaries and note-taking.
- Quality Assurance Efficiency: Assesses the effectiveness and time savings of the Auto QA process in identifying and focusing on high-stake calls that require human review.
- Agent Productivity Metrics: Monitors metrics like the number of calls handled per agent and the efficiency of response, both of which are expected to improve with AI-assisted auto-completing answers and customer replies.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score: Gauges the impact of AI tools on customer satisfaction, reflecting the quality of AI-generated responses and the overall customer experience.
Robust AI Monitoring and Evaluation
As AI begins to evaluate calls, implement robust monitoring systems to ensure AI’s decisions are fair, unbiased, and compliant with legal standards. Regular audits of AI decisions should be mandated to spot any irregularities or biases.
Level 4: AI Empowers Agents Through Knowledge
Who Benefits:
Customers, agents
Goal:
Empower the agent by utilizing Conversational and Generative AI capabilities to break down company-wide data silos and give them instant access to organizational knowledge.
AI Assistants retrieve relevant information from the internal knowledge base to help the agent to respond to customers’ inquiries during a call, eliminating the need for an agent to put the caller on hold to search the knowledge base or call a coworker.
Such a retrieval can be done either automatically by transcribing speech-to-text in real-time, or on-demand, where an agent types the question into a chat-like interface and an AI Assistant retrieves the information from the knowledge base.
By the end of this phase, Generative AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants start to cover the most common Level 1 support calls.
This goes far beyond the top 20-30 questions and answers that chatbots are pre-programmed to answer today.
Requests that these smart chatbots cannot answer are intelligently routed to the next available human agent.
In order to successfully complete this step, the contact centre needs to strategically invest in building an AI-powered knowledge base which is not only used by Gen AI to answer common customer questions, but is also augmented and improved by new AI-generated content.
Critical KPIs:
- Self-Service Resolution Rate: Measures the effectiveness of AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants in resolving Level 1 support calls without escalating to human agents.
- Knowledge Base Usage and Effectiveness: Tracks how often and effectively agents utilize the AI-powered knowledge base to answer customer inquiries, reducing hold times and improving response accuracy.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score Across Channels: Assesses customer satisfaction across various channels, reflecting the success of personalized, AI-powered omnichannel interactions.
- Average Handle Time (AHT) for Complex Inquiries: Monitors the time agents spend on more complex inquiries, which are routed to them after initial AI screening, to assess efficiency in handling advanced issues.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR) for AI-Assisted Interactions: Gauges the percentage of issues resolved during the first interaction by AI assistance, indicating the effectiveness of AI in understanding and addressing customer needs.
- Agent Productivity Metrics for Complex Interactions: Measures the efficiency of agents in handling complex interactions that require human intervention, reflecting the effectiveness of AI in filtering and routing calls.
Data Privacy and Security in AI Assistance
Emphasize the importance of data privacy and security as AI assists agents in real-time. Ensure that AI systems are compliant with data protection regulations (like GDPR) and that customer data is handled securely.
Level 5: Contact Centre Becomes Revenue Centre
Who Benefits:
The entire organization & customers
Goal:
AI-driven analytics can be used outside of contact centre processes to make decisions. For example, a company might identify that they receive too many calls from customers asking to place the order by phone because they were struggling to place it online.
By fixing issues with the online ordering process, the company will reduce the time wasted on such calls and increase revenue (assuming some people were not persistent enough to call a company via phone when they faced issues with the online ordering system).
The organization as a whole benefits from detailed and relevant customer insights extracted, and the contact centre becomes a revenue-generating entity.
This results in the contact centre no longer being a cost centre but a revenue-generating unit within the organization.
Critical KPIs:
- Revenue Generation From Contact Centre Insights: Measures the direct impact of contact centre-driven insights on revenue, such as increased sales due to improvements in online ordering processes identified through customer interactions.
- Customer Insight Utilization Rate: Assesses how frequently and effectively customer insights derived from the contact centre are used to make strategic business decisions across the organization.
- Cost Reduction Through Process Improvements: Monitors the reduction in operational costs achieved by addressing issues identified through contact centre interactions, like streamlining the online ordering process.
- Customer Experience Improvement Index: Evaluates improvements in overall customer experience based on changes implemented from contact centre insights, potentially leading to higher customer retention and acquisition rates.
- Cross-Sell and Up-Sell Success Rates: Tracks the effectiveness of contact centre agents in leveraging customer interactions for successful cross-selling and up-selling, contributing directly to revenue.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS): Continues to measure customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are vital for long-term revenue growth and customer retention.
- First Contact Resolution (FCR) Rate: Still important, this KPI assesses the efficiency of resolving customer issues in the first interaction, which can lead to higher customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs.
- Contact Centre Influence on Product/Service Development: Measures how insights from the contact centre inform and influence product or service development, enhancing market responsiveness and innovation.
- Conversion Rate of Contact to Sale: Tracks how many customer interactions convert into sales, indicating the effectiveness of the contact centre in generating revenue.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Measures the long-term value of customers, influenced by improved customer experiences and services shaped by contact centre insights.
AI Governance and Ethical Standards for Chatbots
Establish governance frameworks to oversee the ethical deployment of chatbots. This includes ensuring that chatbots do not discriminate, mislead, or violate privacy norms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, everyone is at different levels and moves at a different pace — and that’s okay. We developed the Contact Center AI Maturity Model in the hopes of providing a clear path for organizations to drive their contact centre AI adoption forward.
From simply using AI to create call recording transcripts to ultimately becoming a revenue-generating unit, this model helps contact centre leaders navigate the adoption journey.
By embracing AI and leveraging its capabilities, organizations can enhance efficiency, improve customer experiences, and make data-driven decisions.
As the contact centre industry continues to evolve, it is important for decision makers to consider this maturity model as a North Star to unlock the full potential of AI in their operations.
This blog post has been re-published by kind permission of MiaRec – View the Original Article
For more information about MiaRec - visit the MiaRec Website
Call Centre Helper is not responsible for the content of these guest blog posts. The opinions expressed in this article are those of the author, and do not necessarily reflect those of Call Centre Helper.
Author: MiaRec
Published On: 19th Jan 2024 - Last modified: 9th Dec 2024
Read more about - Guest Blogs, MiaRec





 MiaRec is a global provider of Conversation Intelligence and Auto QA solutions, helping contact centers save time and cost through AI-based automation and customer-driven business intelligence.
MiaRec is a global provider of Conversation Intelligence and Auto QA solutions, helping contact centers save time and cost through AI-based automation and customer-driven business intelligence.