Accurately forecasting staffing needs is a key part of running an efficient call centre, and this is where Erlang and the Erlang Calculator come in.
An Erlang calculator is one of the most useful Workforce Management (WFM) tools in the call centre toolkit.
In this article, we’ll explore what Erlang is, how the calculator works, and why it’s a go-to resource for call centre professionals aiming to hit service targets without overspending.
What is an Erlang Calculator?
An Erlang Calculator is a mathematical calculation that allows you to calculate the number of staff that you need for a given number of calls, to meet a given service level.
An Erlang Calculator uses a model based on the Erlang C formula (a derivative of the Poisson distribution) that was designed by the Danish Mathematician A.K. Erlang around 100 years ago, and used for workforce management. The formula is quite involved, but is relatively easy to follow if you studied maths to a reasonable level at school.
You simply enter in the number of phone calls that you receive in a period of time (say per half hour), along with the average duration of the calls and also the service level that you are looking for.
Typical Inputs of an Erlang Calculator
- Number of phone calls
- Time period (e.g. per half hour)
- Average Call Duration (Average Handling Time)
- Service Level (Percentage of calls answered within a period of time, e.g. 80% of calls in 20 seconds)
- Some Erlang calculators also include a shrinkage input.
Typical Outputs of an Erlang Calculator
- Number of agents (advisors) needed to meet the service level target
Formats of Erlang C Calculators
There are two main formats for calculators that use the Erlang model.
1. Excel-based Erlang Calculators
This Excel-based worksheet uses macros, automated input sequences or add-ins, to perform the calculations due to the complexity of the mathematics.
Whilst there are some examples where people have been able to perform the function without using macros (using the Poisson function), these tend to need multiple rows or columns to obtain the required results.
For more information on the Poisson Distribution, read our article: How Is Average Handling Time Distributed? It is not how you think!
Pros
- Easy to build a mini workforce management system.
- Flexible – easy to perform what-if type functions and compare whole days or weeks of calls.
Cons
- Requires macros to be enabled.
- Many do not take account of shrinkage.
- Typically only work up to around 200 agents (700 agents tends to be the absolute limit for double precision floating point numbers).
- Many handmade spreadsheets often contain between 20% and 40% errors
Follow the link for our: Free Erlang C Calculator Excel – Including Shrinkage
Worked Example
Work out the total number of agents (FTE) required for a call volume (including shrinkage)
| Calls | Reporting Period (mins) | Average Call Duration (secs) | Required Service Level (%) | Target Answer Time (secs) | Shrinkage (%) | Agents (FTE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 60 | 180 | 80% | 20 | 35% | 86 |
This uses the Excel Formula:
=AgentsFTE(Calls, Reporting_period, Average_Call_duration, Service_level_percent, Service_level_time, Shrinkage)
For example =AgentsFTE(B30,C30,D30,E30,F30,G30)
This formula is more accurate as it includes shrinkage (holidays, training, meetings, etc.) and therefore gives a more realistic staffing requirement.
For a full explanation of shrinkage, read our article: How to Calculate Shrinkage
2. Online Erlang Calculators
A new generation of Erlang calculators has emerged that are available online.
Watch this video, where Jonty Pearce, the Director of Call Centre Helper explains how the Contact Centre Erlang Online Calculator works:
Pros
- These are freely available online and are easy to test.
- Great for what-if type calculations.
- Some can perform calculations in excess of 700 agents.
- Do not require any software download or potentially harmful macros to be installed on your PC.
Cons
- Most calculators do not take account of shrinkage.
- Limited quality checking.
- Errors over 700 agents. Many online Erlang calculators produce wrong results for large number of agents (see below for how to check this).
Follow the link for our: Call Centre Erlang Staffing Calculator – including Shrinkage
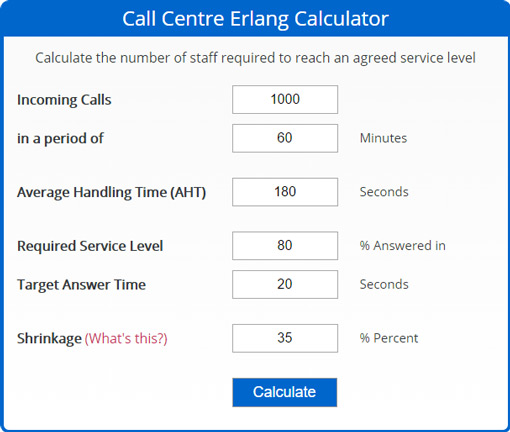
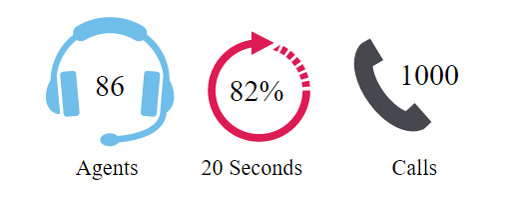
Results
The number of agents needed is 86 agents including 35% shrinkage (56 agents before shrinkage)
This would give a Service Level of 82.3% answered in 20 seconds
The Average Speed of Answer (ASA) would be 12.2 seconds
How to Spot if Your Erlang Calculator is Giving the Wrong Results
STEP 1: Enter the following details into an Erlang calculator
14,200 calls per hour, 180-second call duration, 80% of calls handled in 20 seconds (with no shrinkage if the calculator provides it).
STEP 2: Check that the number of agents equals 721
The correct answer should be 721 agents. Many calculators will confidently predict 711 advisors (often with a Service Level Prediction of nan [not a number]).
STEP 3: Put in 100 fewer calls
So, enter: 14,100 calls per hour, 180-second call duration, 80% of calls handled in 20 seconds (with no shrinkage if the calculator provides it).
Every calculator will then give the right answer of 716 advisors.
This tells you that despite putting in a lower call volume, and keeping all of the other variables the same, the number of advisors has actually increased from 711 to 716, so something must be wrong.
Find some other examples that will enable you to check your Erlang Calculator below.
| Calls Per Hour | Other Inputs | Correct result | Faulty Erlang Calculators Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1410 | Call duration 180 secs, 80% of calls handled in 20 seconds (no shrinkage) | 716 Advisors | 716 Advisors |
| 1420 | Call duration 180 secs, 80% of calls handled in 20 seconds (no shrinkage) | 721 Advisors | 711 Advisors |
| 1500 | Call duration 180 secs, 80% of calls handled in 20 seconds (no shrinkage) | 761 Advisors | 751 Advisors |
| 2000 | Call duration 180 secs, 80% of calls handled in 20 seconds (no shrinkage) | 1011 Advisors | 1001 Advisors |
This process is vital, to ensure that your staffing calculations are as accurate as possible – with overstaffing causing great financial problems and understaffing risking both customer and advisor satisfaction.
With this in mind, we hope that this has been a great introduction to the Erlang Calculator and that we have inspired you to read more of our content – including the three articles below – so you can do the best possible job in staffing your contact centre.
To find out more about applying Erlang mathematics to the contact centre, read our articles:
- How to Work Out How Many Staff You Need in a Contact Centre
- 10 Things You Need When Calculating How Many Contact Centre Advisors You Need
- Erlang Calculation – An Introduction
Author: Jonty Pearce
Reviewed by: Megan Jones
Published On: 29th Mar 2017 - Last modified: 14th Aug 2025
Read more about - Erlang, Editor's Picks, Erlang Calculations, Full Time Equivalent (FTE), Scheduling, Service Level, Shrinkage, Staffing, Workforce Planning


































