Queue position might seem like a small detail, but it plays a big role in shaping the customer’s waiting experience, and in how a contact centre manages its call flow.
From the customer’s perspective, it’s about knowing where they stand in line and how long they might have to wait. Without it, callers are stuck in an “invisible queue”, which can quickly lead to frustration and higher abandon rates.
For contact centre’s, queue position is more than just a courtesy message, it’s a tool for managing customer expectations, improving satisfaction, and even influencing caller behaviour.
In this article we provide a quick guide to help you understand queue positions in the contact centre and the main things to look out for.
What is Queue Position?
A queue position refers to your place in line relative to other customers waiting for service. It tells them how many people are ahead. There are differences in how this is experienced between a physical queue in a bank and a virtual queue in a call centre on the phone.
Queue Position in a Bank or Shop
In a traditional bank, queue position represents where you stand in a physical line of customers waiting to be served at the teller counter. The first person in line is typically the next to be served.
Queue Position in a Call Centre
In a call centre, queue position refers to your place in line while waiting to speak to a customer service agent. As you wait, you might hear an automated message telling you your position in the queue (e.g., “You are the 5th caller in line”).
The queue position is important for managing customer expectations and providing an estimate of how long the customer might have to wait before their call is answered.
It’s a common practice for call centres to provide recorded messages that inform callers about their current queue position or expected wait time to give them an idea of the wait ahead. These announcements use ACD and IVR technology.
Examples of Queue Positions
Your Current Queue Position is 4
In a contact centre, the message “Your current queue position is 4” means that there are three other callers ahead of you waiting to speak to a customer service representative. You are the fourth person in line, and once the agents finish assisting the callers before you, your call will be answered in turn.
Your queue position can change as other callers finish their conversations or leave the queue, bringing you closer to being served.
What Does Queue Position 1 Mean?
In a contact centre, “Your queue position is 1” means that you are next in line to be connected to a customer service representative. There are no other callers ahead of you, and as soon as an agent becomes available, your call will be answered. This indicates that your wait time should be very short.
How Is Queue Position Calculated?
The queue position is calculated in the call routing (ACD system) which answers all calls in the order that they arrive. The ACD system will route the longest-waiting call to the next available agent.
Customers may hear a message that tells them their queue position such as:
“You are 6th in the queue and will be answered as soon as possible.”
VIP Calls
One problem with queue position is that if different priority customers (such as VIP callers) call, in they are placed in the queue above the general queue.
So if a lower-priority customer is 5th in the queue, at the next announcement they may find that they are 6th in the queue. This is difficult to explain to customers and can decrease customer satisfaction.
Queue Position vs Invisible Queue
Queue position is designed to solve the invisible queue situation.
In a real-life queue you start unhappy and tend (assuming the queue is moving) to get happier as you progress towards the front. In an invisible queue you start happy and get less happy as the call progresses.
What Is an Invisible Queue?
An Invisible Queue is a call centre queue where the caller is not made aware of how they are progressing.
Psychologically, a real-life queue and a call centre queue are quite different.
Estimated Wait Time (EWT)
One similar metric is the Estimated Wait Time.
This tries to predict how long a customer will need to wait in queue before they are answered, for example customers may hear a message that says:
“Thank you for calling. We are busier than we expected today. You are being held in a queue and we expect you to be answered in 5 minutes.”
This is quite popular, but in smaller call centres can be rather inaccurate.
How Is Estimated Wait Time Calculated?
There are two ways of calculating Estimated Wait Time.
- Last Call Waiting Time (LCWT). This looks at how long the last person had to wait. This give a reasonable estimate for how long the next person will have to wait.
- Calculate the number of calls in the queue, multiply it by Average Handling Time and divide it by the number of agents available.
One of the big problems with Estimated Wait Time is that it depends on the actual length of the calls in progress.
So, if the calls in progress are much longer than average, then the actual wait time could exceed the Estimated Wait Time.
Queue Position in Customer Service
While queue position is popular in contact centres, it can also be used in other areas of customer service.
For example, AO can give you a queue position by showing how many deliveries the driver has to make before they arrive at your house.
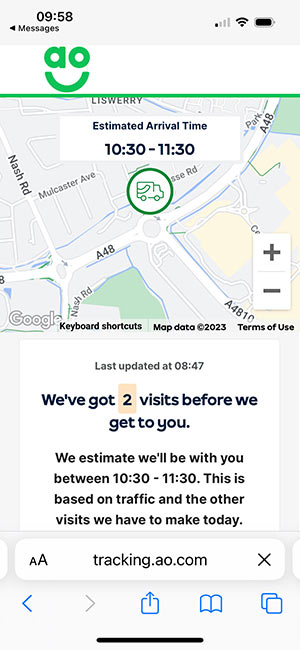
For ideas we picked up on a site visit to the AO contact centre in Bolton, read our article: 17 Things You Can Learn From the AO Contact Centre
Average Queue Times in Contact Centres
ASA (average speed of answer) is a key part of a contact centre’s SLA (Service Level Agreement) and represents a guarantee to answer ‘X’ number of calls in ‘Y’ amount of time.
The global average for ASA is roughly 28 seconds. The 80/20 rule (also known as the Pareto Principle), whereby 80% of calls are answered within 20 seconds, is often used by contact centres as well.
To help you find the ideal wait time and service level in a queue for your contact centre, read our article: What Is an Acceptable Call Centre Waiting Time?
Implementing Queue Position Announcements
A queue position announcement refers to a pre-recorded audio message that customers listen to while waiting on hold.
This message provides them with information about their position in the queue, indicating the number of callers ahead and an estimated wait time before they will be connected with a live agent.
A lot can depend on the timing of these messages. Too frequent and you can risk irritating your customers by creating a feeling that they aren’t moving through the queue positions.
A key metric to observe when implementing queue position announcements is your Call Abandon Rate, which refers to the length of time before a customer hangs up without connecting to an agent.
Call Abandon Rate varies by industry, but from research of our own users in our annual survey “What Are Contact Centres Doing Right Now”, a third of callers are too impatient to wait more than one minute.
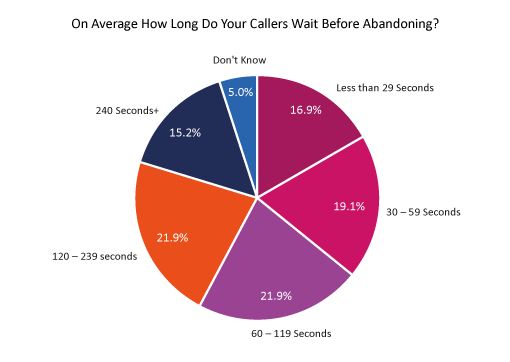
If you are looking to improve your abandon rates, read our article: How to Bring Down Your Call-Abandon Rates
Does a Callback Feature Complement Queue Positioning?
Yes. Instead of waiting on hold, customers can request a callback from a live agent. The caller can then go about their normal activities without losing their position in the queue. When an advisor is available the system will call the customer and connect then to the advisor.
If you want to find out more about queues and improving customer experience, read these articles next:
- ACD ‘Call In Queue’ Announcements
- 19 Contact Centre Queueing Strategies
- Industry Average- Acceptable Wait Time?
Author: Xander Freeman
Reviewed by: Jonty Pearce
Published On: 13th Sep 2023 - Last modified: 2nd Sep 2025
Read more about - Technology, Automatic Call Distributor (ACD), Call Routing, Queues



































